Tel:86-13421392566

UV light has long been associated with sunburns, tanning, and sterilization. But did you know that ultraviolet radiation also plays an important role in plant growth and development? Gardeners, farmers, and researchers are now asking a critical question: How does UV light affect plants, and can it improve crop quality?what is the best uv light for plants?
This article provides a complete breakdown of how UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C light influence plants, the benefits and risks of UV exposure, how artificial UV lamps are used in modern agriculture, and the future of UV light for plants in controlled-environment farming.
What is UV Light?
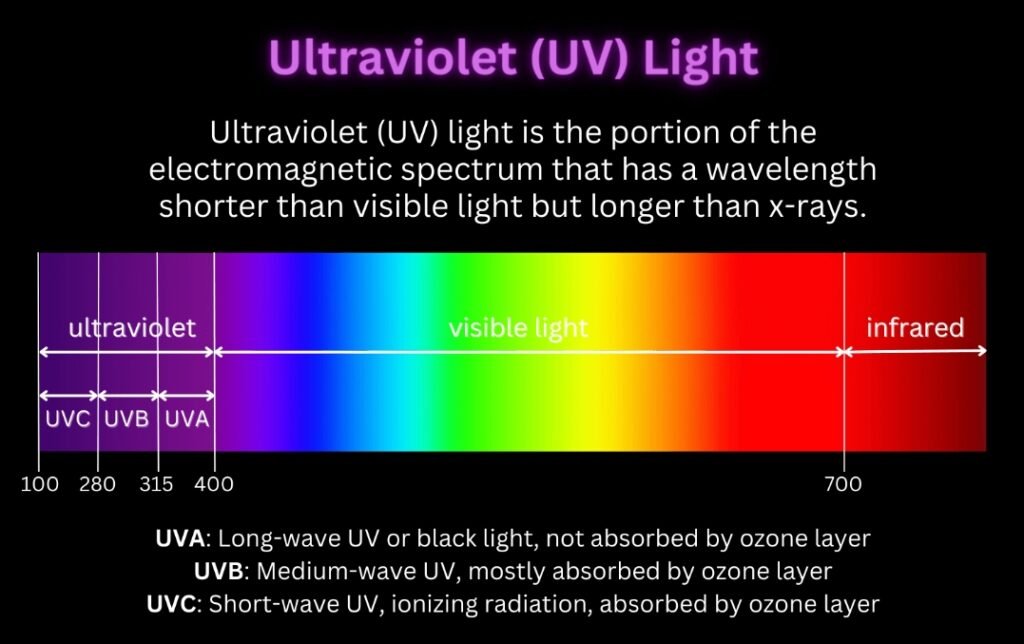
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a type of electromagnetic radiation just beyond the violet end of visible light. It is invisible to the human eye but has powerful biological effects.
UV light is classified into three main types:
- UVA (315–400 nm): Lowest energy, penetrates deeply, influences plant signaling and secondary metabolites.
- UVB (280–315 nm): Medium energy, strongly affects plant morphology, stress responses, and defense compounds.
- UVC (100–280 nm): Highest energy, naturally blocked by the ozone layer, used artificially for sterilization.
Understanding these categories is crucial to analyzing how UV light for plants.
How Plants Perceive and Respond to UV Light
Plants are not passive under UV radiation. They have evolved UV receptors and protective mechanisms to manage and even benefit from UV exposure.
- Photoreceptors: Plants detect UVA and UVB through proteins like UVR8, triggering protective and developmental pathways.
- Secondary metabolites: Under UV stress, plants increase flavonoids, anthocyanins, and phenolic compounds that act as sunscreens.
- Morphological changes: UV influences leaf thickness, pigmentation, and stem elongation.
- Defense signaling: UV light can “prime” plants against pathogens and herbivores.
These adaptations suggest that UV radiation, in controlled amounts, can enhance plant resilience and nutritional quality.
Benefits of UV Light for Plants
1. Improved Photosynthesis and Growth (Mainly UVA)
- UVA wavelengths (around 365–395 nm) support photosynthetic efficiency by energizing accessory pigments.
- Studies show that plants grown with supplemental UVA often display healthier growth, greener leaves, and stronger stems.
2. Higher Production of Secondary Metabolites (UVB)
- UVB stimulates the accumulation of flavonoids, terpenes, and phenolic compounds, which act as natural sunscreens.
- In crops like grapes, tomatoes, and cannabis, this leads to better flavor, aroma, and nutritional quality.
3. Enhanced Plant Defense
- UV exposure strengthens plant cuticles and cell walls, making them more resistant to fungal infections and insect pests.
- The induced secondary metabolites often have antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, improving shelf life.
4. Increased Nutritional Value
- Crops exposed to UV light often contain higher levels of vitamin C, antioxidants, and phytonutrients.
- This adds value to fruits, vegetables, and herbs marketed for health-conscious consumers.
5. Stress Conditioning for Resilience
- Controlled UV stress helps plants build tolerance to heat, drought, and disease, crucial for climate change adaptation.
Risks of Excessive UV Light
While moderate UV exposure is beneficial, too much can harm plants.
- UVA overexposure: Can cause oxidative stress and slow growth.
- UVB overexposure: Leads to DNA damage, reduced photosynthesis, leaf curling, and stunted development.
- UVC exposure: Directly damages cells; in agriculture, it is used only as a sterilization tool, not for growth.
The key is balance—providing enough UV to stimulate positive responses without overwhelming the plant.
Applications of UV Light for plants in Modern Agriculture
1. Indoor Farming and Greenhouses
- UVA and UVB lamps are integrated into LED grow systems to mimic sunlight.
- Controlled UV supplementation improves crop quality in tomatoes, lettuce, strawberries, and cannabis.
2. Crop Protection with UVC
- UVC lamps are used in greenhouses to sterilize surfaces, water, and air, reducing fungal spores and bacterial contamination.
- UVC treatment also delays mold growth post-harvest, extending storage life.
3. Flavor and Nutritional Enhancement
- Wine grapes grown with UVB exposure develop richer flavors and higher antioxidant content.
- Herbs like basil and mint show stronger aromas when exposed to supplemental UV.
4. Sustainable Agriculture
- UV supplementation reduces reliance on chemical pesticides and fungicides, aligning with organic and eco-friendly farming practices.
How to Use UV Light Safely for Plants
- uv light for plants,Select the right wavelength:
- Use UVA (365–395 nm) for photosynthesis support.
- Add UVB (280–315 nm) in small doses for quality improvement.
- Reserve UVC (254 nm) only for sterilization, not direct plant exposure.
- uv light for plants,Control exposure time:
- UVA: 8–12 hours daily as part of the grow light spectrum.
- UVB: 15–60 minutes per day, depending on plant type.
- UVC: Seconds to minutes for disinfection, not growth.
- uv light for plants,Adjust intensity based on species:
- Leafy greens tolerate less UV than hardy herbs or fruiting plants.
- Sensitive plants may need UV filters to avoid leaf burn.
- Safety for humans:
- Always wear protective glasses when working near UV lights.
- Use shielding to avoid direct UVC exposure.
Future of UV Light in Plant Science
The future looks promising as LED UV technology continues to advance. Unlike traditional mercury UV lamps, LED UV offers:
- Precise wavelength targeting (e.g., 280 nm for UVB, 365 nm for UVA)
- Longer lifespan and energy efficiency
- Compact, customizable modules for greenhouses and vertical farms
- No toxic mercury, making them eco-friendly
As more studies confirm the benefits of UV light, we may see customized UV grow lights tailored for specific crops—boosting flavor, nutrition, and resistance naturally.uv light for plants
Conclusion
So, is UV light good for plants?uv light for plants
Yes—when used correctly. UVA and UVB light play crucial roles in improving photosynthesis, enhancing flavors, boosting nutritional compounds, and strengthening plant defenses. UVC light, while not for growth, is a powerful sterilization tool in modern farming.
By carefully balancing intensity, duration, and spectrum, UV light can transform plant cultivation—making crops healthier, tastier, and more sustainable.
As agriculture moves toward a future shaped by technology and sustainability, UV light is becoming a key ally for growers worldwide.







