Tel:86-13421392566
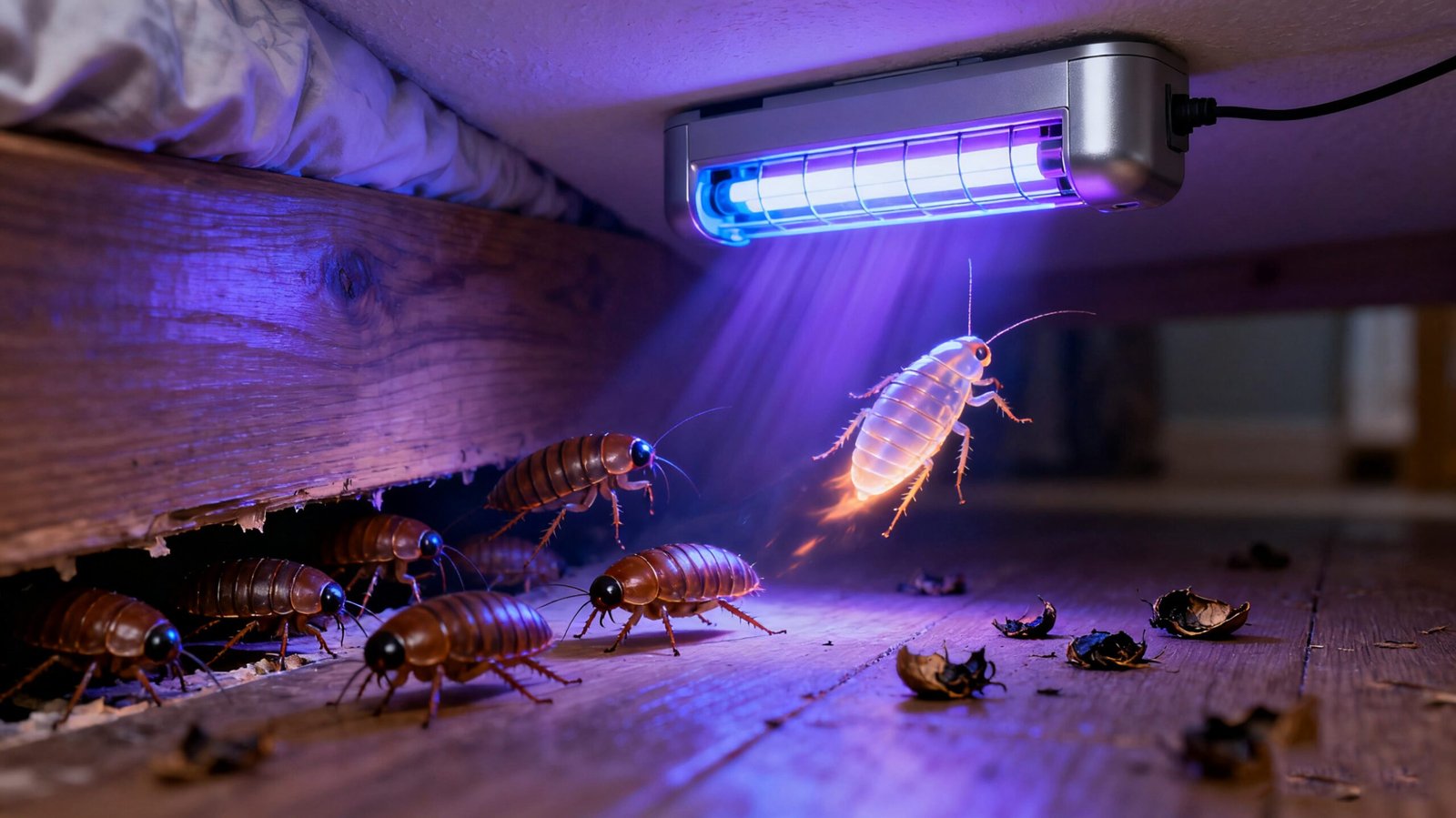

Bed bugs are among the most persistent and frustrating pests that infest homes, hotels, dormitories, and even public transportation. Known for their ability to hide in the smallest cracks and reproduce quickly, they are notoriously difficult to eliminate once established. In recent years, many people have turned their attention to innovative, chemical-free methods of pest control. One of the most commonly asked questions is: Does UV light kill bed bugs?
The short answer is yes—certain wavelengths of UV light, particularly UVC, can kill bed bugs by damaging their DNA. However, the effectiveness depends on many factors, including direct exposure, intensity, and duration. This guide explores bed bugs’ biology, the science behind UV light, the best wavelengths for extermination, the limitations of UV technology, and how LED UV is shaping the future of pest control.
What Makes Bed Bugs So Difficult to Kill?
Despite decades of pest control innovations, bed bugs remain one of the toughest insects to eradicate. Their biology and behavior give them natural advantages against most treatments.
The biology of bed bugs
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, wingless insects that feed on human blood. Adult bed bugs are roughly the size of an apple seed—about 5 to 7 millimeters long—and reddish-brown in color. They have flat, oval-shaped bodies that allow them to hide in tiny crevices such as mattress seams, furniture joints, or behind wallpaper.
Key biological traits:
- Feeding habits: Bed bugs feed primarily at night, using an elongated beak to pierce human skin and extract blood.
- Reproductive capacity: A single female can lay between 200–500 eggs in her lifetime, ensuring infestations grow rapidly.
- Survival skills: Bed bugs can live for several months without feeding, waiting patiently for a host.
- Lifespan: Under the right conditions, bed bugs live 6–12 months, long enough to sustain and expand infestations.
Why infestations spread quickly
Bed bugs spread quickly due to several reasons:
- Hitchhiking ability: They attach to luggage, clothing, or furniture, allowing them to move from one location to another.
- Resistance to pesticides: Many populations have developed resistance to common insecticides, reducing treatment success rates.
- Stealth: Their nocturnal behavior and ability to hide in cracks make early detection difficult.
- Rapid reproduction: Even a few surviving insects can reestablish a large population within weeks.
These factors explain why bed bugs are among the most challenging pests to control, and why alternative solutions like UV light are gaining attention.
How UV Light Works Against Bed Bugs,does uv light kill bed bugs?
To understand whether UV light can kill bed bugs, we need to explore how UV radiation interacts with living organisms.Does UV light kill bed bugs
The science of UV radiation
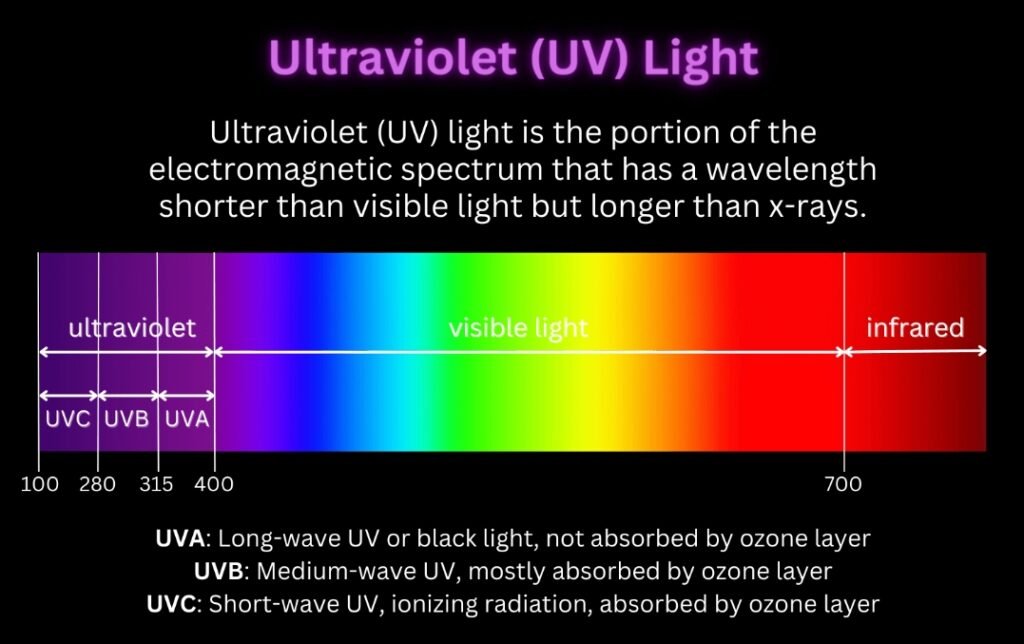
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays. It is divided into three main categories:
- UVA (315–400 nm): The least harmful type, responsible for tanning and widely used in black lights.
- UVB (280–315 nm): More energetic, responsible for sunburn and DNA damage in skin cells.
- UVC (200–280 nm): The most energetic form, capable of destroying microorganisms, viruses, and insects by damaging their DNA.
UVC is particularly known for its germicidal properties and is used in water purification, air sterilization, and surface disinfection.
DNA damage and pest sterilization
does uv light kill bed bugs?When bed bugs are exposed to UVC light, photons penetrate their outer shell and strike their DNA and cellular structures. The radiation causes thymine dimers, a type of DNA damage that prevents the insect from reproducing or functioning properly. Prolonged exposure results in sterilization or death.
This process is similar to how UVC sterilizes bacteria and viruses, making it effective against a wide range of organisms, including insects.
Does UV Light Kill Bed Bugs?Best UV Wavelengths for Killing Bed Bugs
Not all UV light is equally effective. The effectiveness depends on wavelength, intensity, and exposure duration.
UVA: 365 nm, 395 nm for detection
UVA wavelengths such as 365 nm and 395 nm are not strong enough to kill bed bugs but are useful for detection. Bed bug stains, eggs, and shed skins fluoresce under UVA light, making infestations easier to spot in dark areas.
Applications of UVA flashlights:
- Detecting bed bug droppings on mattresses and sheets
- Spotting eggs or shed exoskeletons
- Assisting in inspection before and after treatment
UVC: 254–280 nm for extermination
The most effective UV range for killing bed bugs is 254–280 nm (UVC). At this wavelength, UV light penetrates and destroys DNA.does uv light kill bed bugs
- 254 nm: Traditionally produced by mercury vapor lamps, highly effective for sterilization.
- 265–275 nm: The peak germicidal range, often produced by modern UVC LEDs.
- Exposure time: Requires direct exposure for several seconds to minutes to achieve lethal effects.
Far-UVC: 222 nm, the next innovation
A newer type of UVC, known as far-UVC (222 nm), has gained attention because it kills pathogens without penetrating human skin or eyes. While research is ongoing, it may offer a safer option for continuous use in occupied spaces.
Though studies on far-UVC’s impact on insects like bed bugs are limited, it represents a promising development in pest control.does uv light kill bed bugs

Limitations of UV Light in Bed Bug Control
While UV light is powerful, it is not a perfect solution for bed bug infestations.
Direct exposure requirement
does uv light kill bed bugs,UV light only works if it directly hits the insect. Bed bugs hiding deep inside furniture, mattresses, or cracks may not be exposed, reducing effectiveness.
Safety concerns with UVC
UVC light is harmful to human skin and eyes. Prolonged exposure can cause burns or eye damage. Protective equipment and safety measures are required when using UVC devices.
No residual effect
Unlike chemical treatments, UV light leaves no lasting effect. Once the light is turned off, the environment is no longer hostile to bed bugs. This means repeated treatments are necessary.does uv light kill bed bugs
LED UV vs Traditional UV Lamps: Which Works Best?
Both LED UV and traditional mercury UV lamps have applications in pest control, but each has distinct advantages.
Advantages of traditional UV lamps
- Produce high-intensity 254 nm UVC light
- Proven track record in sterilization (hospitals, labs, water treatment)
- Effective for large-scale disinfection
Drawbacks include:
- Bulky size
- Contain mercury, posing environmental risks
- Shorter lifespan compared to LEDs
- Higher power consumption
Why LED UV is the future
LED UV technology has advanced significantly and offers many benefits:
- Custom wavelengths: LEDs can be designed for 265–275 nm, the most germicidal range.
- Energy efficiency: Consume less power than traditional lamps.
- Longevity: Last up to 25,000–50,000 hours.
- Compact design: Easy to integrate into portable flashlights or handheld sanitizers.
- Eco-friendly: Mercury-free and safer for the environment.
For bed bug detection and control, LED UV flashlights and UVC devices are rapidly becoming the preferred option.
How to Use UV Light for Bed Bug Detection and Treatment
To maximize the benefits of UV technology, it should be applied strategically.does uv light kill bed bugs
Inspection with UV flashlight
Use a 365 nm or 395 nm UVA flashlight to scan mattresses, furniture, and walls. Look for:
- Black spots (bed bug feces)
- Whitish eggs in cracks or seams
- Shed exoskeletons or live insects
This helps identify infested areas before treatment.
Disinfection with UVC devices
Apply a 254–275 nm UVC lamp or handheld device directly onto exposed bed bugs. Hold the light close for several seconds to ensure lethal exposure.
While this won’t reach bugs hidden in deep crevices, it is effective for surface-level treatment.does uv light kill bed bugs
Combining UV with other treatments
does uv light kill bed bugs?UV light should be part of an integrated pest management (IPM) strategy:
- Heat treatment: Raising room temperature to 120°F (49°C) kills hidden bugs.
- Vacuuming: Physically removes bugs and eggs from surfaces.
- Encasements: Mattress and box spring covers prevent reinfestation.
- Professional pest control: Ensures thorough elimination.
UV Technology: The Future of Pest Management
With rising resistance to pesticides, the demand for safer, eco-friendly solutions is growing.does uv light kill bed bugs
Eco-friendly pest control
UV light offers a chemical-free method of killing pests, making it safer for homes, hospitals, schools, and hotels. Unlike insecticides, it leaves no chemical residue and does not contaminate the environment.does uv light kill bed bugs
Safer alternatives to chemicals
While UV is not yet a complete replacement for traditional pest control, it is a valuable addition. Future advancements in LED UVC and far-UVC technology may allow for continuous, safe operation in occupied spaces, making bed bug control easier and more effective.does uv light kill bed bugs
Conclusion
So, does UV light kill bed bugs?
Yes. UVC light in the 254–280 nm range can kill bed bugs by damaging their DNA and preventing reproduction. However, effectiveness depends on direct exposure, intensity, and treatment strategy.
While bed bugs remain difficult to eradicate due to their hiding behavior and resilience, UV technology is a powerful tool when combined with heat, vacuuming, and professional pest control.
With the rise of LED UV devices, pest management is entering a new era—one that is safer, greener, and more efficient.
For anyone battling bed bugs, UV light is not a magic bullet, but it is a critical weapon in the fight for a pest-free environment.






