Tel:86-13421392566
Introduction
Tanning has been popular for decades, symbolizing health, beauty, and confidence. But one of the most common questions people ask is: what UV is good for tanning? The science behind tanning is tied to ultraviolet (UV) light, a type of electromagnetic radiation from the sun and artificial tanning lamps.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about tanning, UV rays, the risks and benefits, safe practices, and modern alternatives. Whether you prefer sunbathing or tanning beds, understanding UV light is key to making safe and informed decisions.what UV is good for tanning
What Is UV Light?
Ultraviolet (UV) light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, just beyond the range visible to the human eye. Its wavelengths range between 100 and 400 nanometers (nm), divided into three categories:
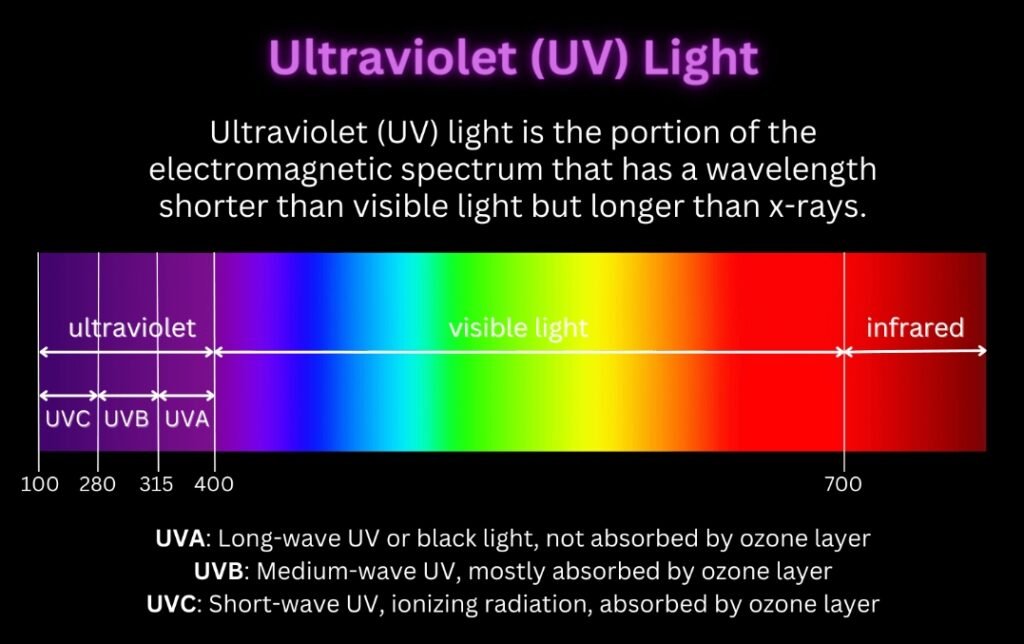
UVA (315–400 nm)
- The longest wavelength.
- Penetrates deep into the skin.
- Main contributor to skin tanning and aging.
UVB (280–315 nm)
- Medium wavelength.
- Stimulates melanin production.
- Responsible for sunburns but also essential for tanning.
UVC (100–280 nm)
- Shortest and most dangerous UV rays.
- Completely absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Not used for tanning.
So, when asking what UV is good for tanning, the answer is primarily UVA and UVB.
How Tanning Works
Tanning occurs when the skin reacts to UV exposure. The body produces melanin, a natural pigment that protects skin cells from UV damage.
The Role of UVA in Tanning
- Triggers immediate pigmentation by darkening existing melanin.
- Produces a faster tan but fades quickly.
- Contributes more to long-term skin aging.
The Role of UVB in Tanning
- Stimulates new melanin production.
- Causes delayed tanning that lasts longer.
- Also increases vitamin D synthesis.
In short: UVA gives quick results, UVB builds lasting color. Together, they determine how your tan looks and how long it lasts.

What UV Is Good for Tanning?
Now we answer the central question: what UV is good for tanning?
- UVA rays are good for creating an immediate tan.
- UVB rays are good for stimulating melanin production and ensuring the tan lasts longer.
- The best tanning occurs when there is a balanced mix of UVA and UVB exposure.
Commercial tanning lamps often mimic this combination, offering around 95% UVA and 5% UVB for controlled tanning results.
Natural Sunlight vs. Tanning Beds
Sunlight
- Provides natural UVA and UVB rays.
- Stronger UV exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Seasonal and geographical factors affect UV intensity.
Tanning Beds
- Use specialized bulbs to deliver controlled UV radiation.
- Often designed with higher UVA levels for fast results.
- Can increase risks if not used responsibly.
When evaluating what UV is good for tanning, many experts recommend short, safe exposures to natural sunlight over tanning beds, since beds often deliver concentrated UVA that accelerates skin aging.
Benefits of Tanning
Vitamin D Production
UVB rays stimulate vitamin D production, essential for bone health, immunity, and mood regulation.
Cosmetic Appeal
A tanned complexion is considered attractive and healthy-looking by many cultures.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Relief
Exposure to sunlight can improve mood and energy levels.
Risks of UV Tanning
Skin Damage
Overexposure to UVA and UVB can damage skin cells, leading to premature aging and wrinkles.
Sunburn
Excess UVB exposure causes painful burns, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer
Both UVA and UVB are classified as carcinogens, with prolonged exposure raising the risk of melanoma and non-melanoma cancers.
Eye Damage
Unprotected eyes may develop cataracts or photokeratitis.
This is why understanding what UV is good for tanning is important—responsible exposure is key.
Safe Tanning Practices
Limit Exposure
- Start with 10–20 minutes depending on skin type.
- Avoid midday hours when UV is strongest.
Use Sunscreen
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+).
- Protects against UVA and UVB while allowing gradual tanning.
Wear Protective Gear
- Sunglasses with UV protection.
- Hats and clothing for extended sun sessions.
Gradual Tanning
- Build your tan slowly over time.
- Prevents burns and promotes longer-lasting color.
Alternatives to UV Tanning
Self-Tanning Lotions
- Provide a bronzed look without UV exposure.
- Use dihydroxyacetone (DHA) to darken skin safely.
Spray Tans
- Professional application for even results.
- Safe for skin with no UV risk.
Bronzing Makeup
- Temporary option for events.
- Washes off easily.
These alternatives offer a glow without the risks tied to what UV is good for tanning.
The Future of Tanning Technology
Innovations in tanning focus on reducing health risks while still delivering a bronzed appearance.
UV LED Lamps
- Research is ongoing into UV LED tanning systems.
- Potential for more precise UVA/UVB balance.

Far-UVC Technology (222 nm)
- Currently used in sterilization.
- Studied for safe skin applications in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does UVA or UVB tan better?
- UVA tans quickly but fades.
- UVB builds deeper, longer-lasting color.
- Best results come from a UVA + UVB combination.
What UV index is best for tanning?
- A UV index between 3–5 is considered safe for gradual tanning.
- Above 6, risk of sunburn increases.
Can you tan with sunscreen?
Yes. Broad-spectrum sunscreen allows tanning while reducing the risks of burns and premature aging.
Are tanning beds safer than sunlight?
No. Tanning beds often emit higher concentrations of UVA, which increases aging and cancer risks.
what UV is good for tanning







